2. Cerebrum- takes information and processes it
cerebellum- motor control and muscle movement
brain stem- connects to spinal cord, breathing, digestion
meninges- separates blood and brain
3. Insulation around the neuron. Allows faster communication
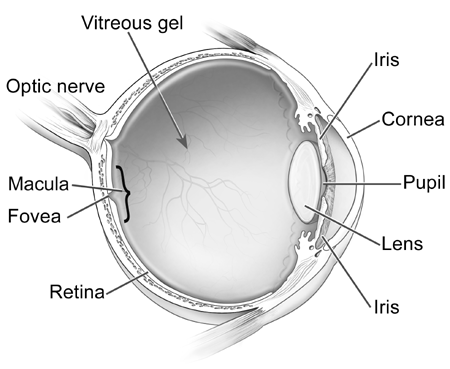
4.


5. Thalamus- relays sensory information, feels pain
Optic Nerve- connects the brain to the eye
Medulla Oblongata- controls heart and lungs
Pons- links the medulla oblongata to the thalamus
Midbrain- vision, hearing, and motor control
Corpus Collusum- joins the two hemispheres of the brain
Hypothalamus- controls the autonomic nervous system
6.


Relate and Review:
This lab was very interesting. I'm getting better at labs in terms of being able to find things easier and also not being grossed out. I think the most interesting part was seeing the corpus callosum separating the two distinct hemispheres of the brain. Doing a lab is different than reading a textbook or watching a vodcast because it isn't color coded and labeled. This leaves a lot of grey area for error, however once you focus on what you're looking for you're able to find it.